What new UK EV charging standards are emerging in 2026?
ISO 15118 and OCPP 2.1 are fast becoming industry expectations, not just nice-to-haves. These sit alongside updated regulatory requirements, including the Public Charge Point Regulations 2023 and Smart Charge Points Regulations 2021. Together, they're reshaping what "compliant" means for any charger destined for the UK market, whether it's a domestic wallbox or a high-power public rapid charger.
How does ISO 15118 / Plug & Charge affect design?
ISO 15118 fundamentally changes how vehicles and chargers communicate, enabling secure, automatic authentication without apps or RFID cards. This requires integrating certificate management systems, implementing secure hardware elements for cryptographic operations, and developing robust firmware layers to handle the ISO 15118 state machine. You'll also need partnerships with PKI providers and comprehensive interoperability testing across different vehicle manufacturers to ensure reliable handshakes in real-world conditions.
Do I still need OCPP 1.6 support?
Yes, OCPP 1.6 remains widely deployed and won't disappear overnight. However, you should be actively preparing for migration to OCPP 2.0.1 or 2.1 (for V2G support), which offer native support for smart charging, enhanced security frameworks, and better integration with ISO 15118. The smartest approach is a dual-stack implementation with feature flags, allowing you to serve legacy networks whilst positioning yourself for next-generation CPO requirements.
What smart charging rules apply now?
Since June 2022, all new domestic and workplace chargers in Great Britain must include default off-peak scheduling (avoiding 08:00–11:00 and 16:00–22:00 on weekdays), randomised start delays up to 30 minutes to prevent grid stress, and mandatory cybersecurity controls including secure communications and password protection. These are legal requirements that apply to every residential and workplace installation, with enforcement mechanisms already in place.
How can Versinetic help?
Through our field-tested ISO 15118 stack, proven OCPP integration modules, and comprehensive compliance consultancy tested across UK and European projects, Versinetic accelerates your route to market. We've worked directly with OEMs, charge point integrators, and network operators for over a decade, giving us practical insight into what actually works in deployment, not just what looks good in specifications. Our modular approach means you can integrate exactly what you need, when you need it, without wholesale redesigns.
Don't Let More Charging Standards Changes Cause Your Product Line to Stall
UK charging standards are in rapid flux. Between new regulations (Public Charge Point Regulations, Smart Charge rules) and changing protocol versions, charger manufacturers now face greater compliance complexity than ever before.
The UK is also deciding whether to adopt the EU regulations mandating 15118-20 compliance by January 2027.
The cost of lagging can be steep. Wasted R&D, stranded products, difficult retrofit paths, and lost market opportunities as CPOs and fleet operators demand standards-compliant hardware.
It’s clear that these emerging standards will shape which products make it to market, and which stall in certification or field deployment.
In this article we cut straight to what matters for design, firmware, testing, standards alignment and strategic planning.
No filler, just what your engineering teams need.
Table of Contents
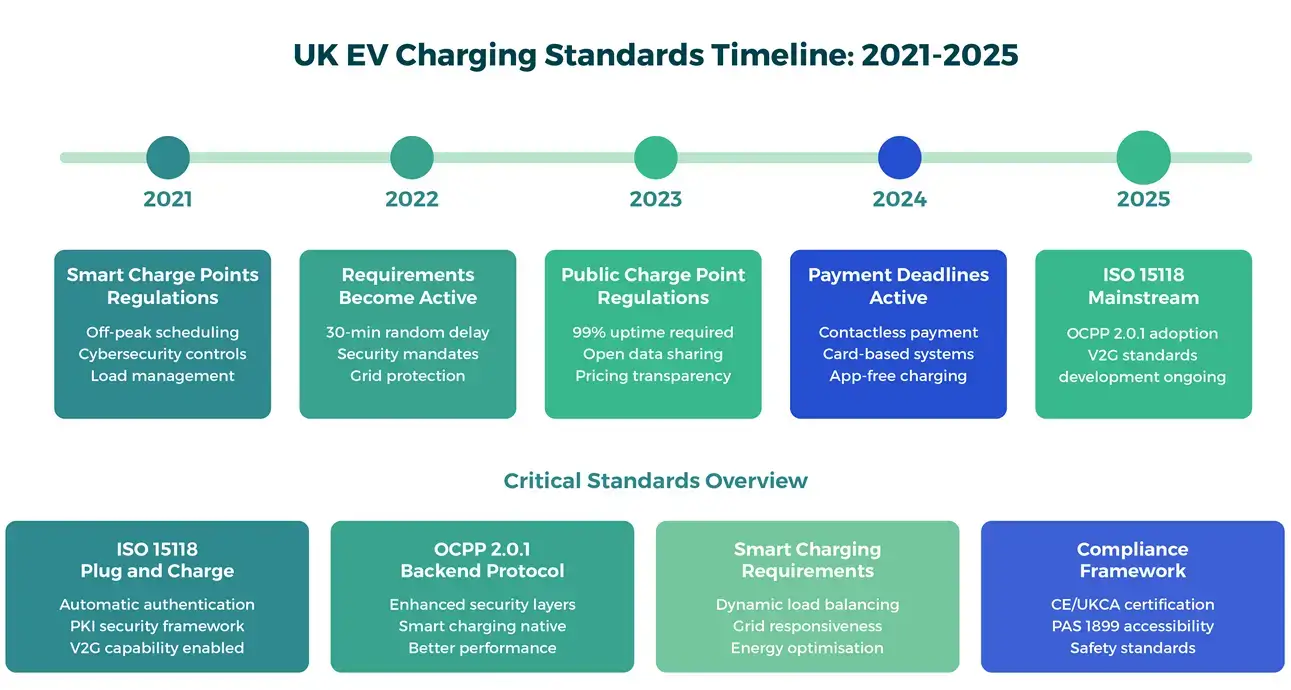
What Are the Key EV Charging Standards Shaping the UK Market?
The UK market revolves around a handful of international standards that govern every level of charger behaviour:
- ISO 15118-2 – defines vehicle-to-charger communication, enabling Plug & Charge
- ISO 15118-20 – extends vehicle-to-charger communication, and enables V2G
- SESS – Smart Secure Energy Systems: a regulatory framework for load controllers
- OCPP 1.6 → 2.0.1 / 2.1 – handles data exchange between chargers and back-offices
- IEC 61851 / 62196 – specify electrical safety and connector formats
- Smart Charge Points Regulations 2021 – make cybersecurity and off-peak scheduling mandatory
- Public Charge Point Regulations 2023 – require payment, reliability and open-data transparency
- PAS 1899 – ensures accessible public-charging design
Together, these create the compliance framework for every charger sold or installed in Britain.
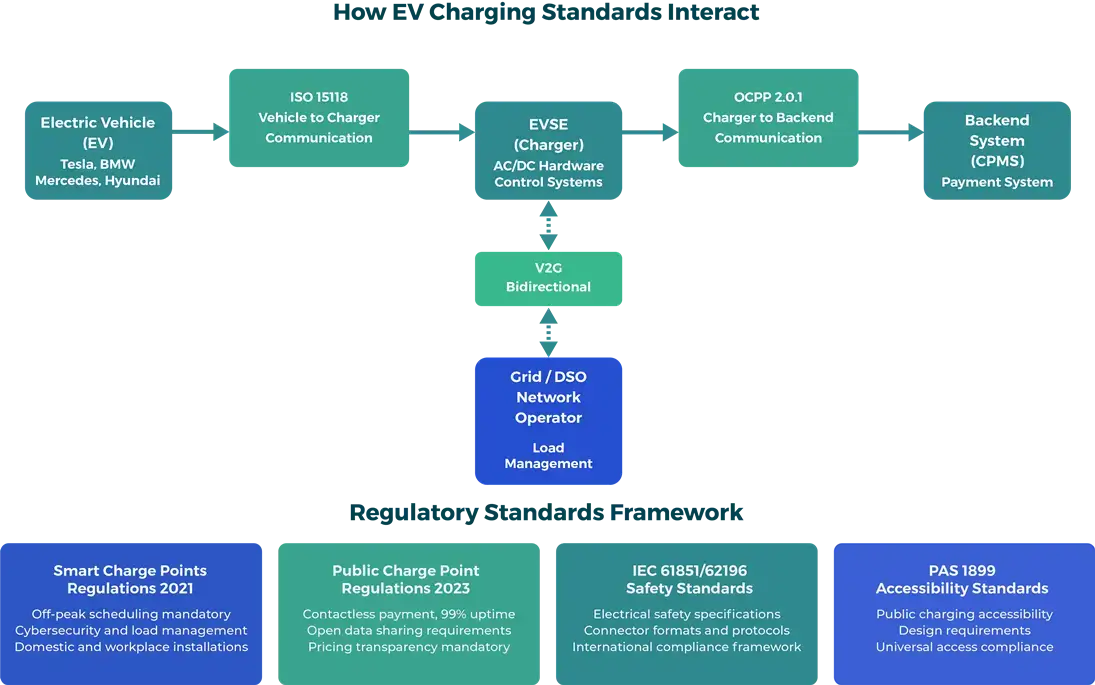
How Will ISO 15118 Change Charger Communication and Functionality?
ISO 15118 is no longer classed as “future tech” and is fast becoming a baseline expectation, especially for DC and high-end AC stations.
- It enables Plug & Charge, where the vehicle and charger authenticate automatically, handling payment and identity securely via certificate exchange
- It supports smart charging, bidirectional energy (V2X), scheduling, load management and grid codes
- It requires secure PKI infrastructures, TLS, and certificate management
Key Implications for Manufacturers
- You’ll need to integrate or partner with a PKI / certificate authority system. Each global region operates multiple PKIs with their own Certificate Authorities. In Europe, Hubject operates one of the major PKIs for Plug & Charge. Versinetic can help you navigate these ecosystems and reduce integration burden.
- Firmware must implement the ISO 15118 state machine for the use cases you’re targeting, whether that’s basic Plug & Charge, V2G bidirectional energy transfer, or smart grid interaction.
- You’ll need hardware layers such as secure elements or crypto co-processors to perform cryptographic operations efficiently without overwhelming your main processor. You also need a PLC (PowerLine Communications module).
- Interoperability testing is essential. Different EV brands will have implementation quirks or partial support for various ISO 15118 features. Real-world testing with multiple vehicle manufacturers is non-negotiable.
Common implementation challenges include:
- Certificate storage and handling across different PKI frameworks
- PKI infrastructure complexity and ongoing cost management
- Additional hardware performance requirements for crypto operations
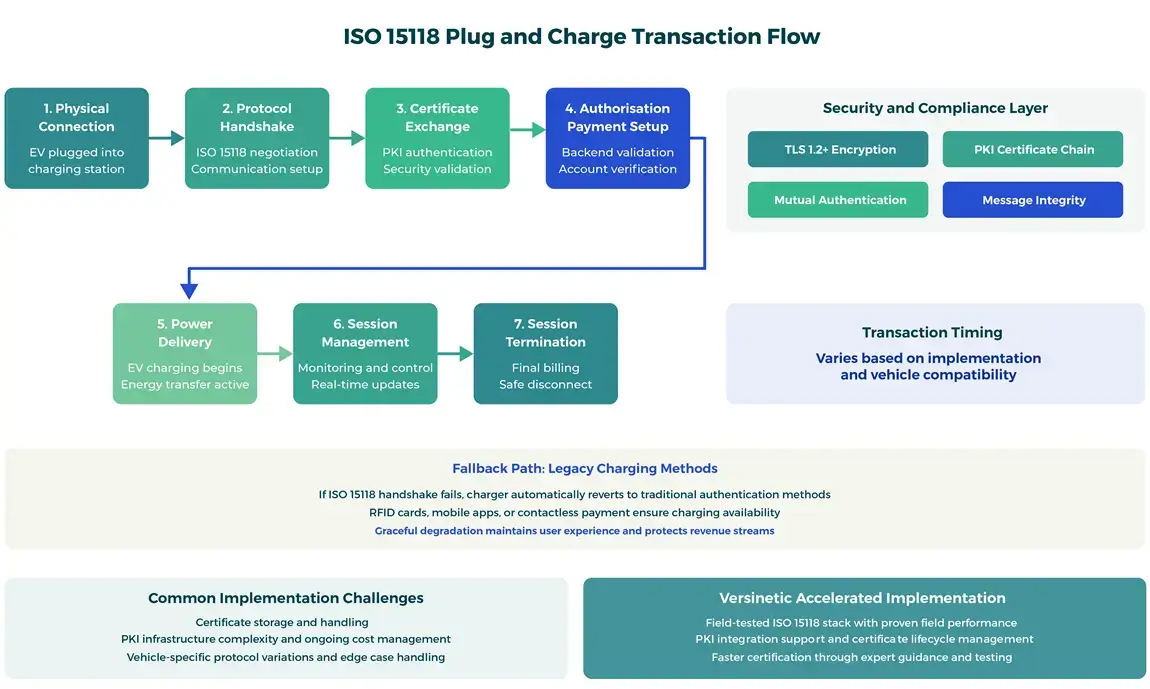
Versinetic’s Role
Our field-tested ISO 15118 stack can serve as the reference firmware your team builds onto.
We’ve proven our implementation with CSMS (Charge Station Management Systems), giving you a significant jumpstart and reducing time-to-market by months.
Do the UK Regulations Now Require Smart and Interoperable Chargers?
In short, yes. Many new installations must already satisfy smart- and payment-related obligations.
Smart Charge Points Regulations 2021 (Domestic / Workplace)
Since 30 June 2022, all new domestic or workplace EV chargers in Great Britain must include:
- Default off-peak charging scheduling (avoiding 08:00–11:00 & 16:00–22:00 on weekdays unless overridden by the user)
- Randomised delay up to 10 minutes (with the provision of extending it up to 30 minutes in the future) to prevent system stress from many chargers starting simultaneously
- Cybersecurity controls, including secure passwords, encryption, and secure communications (referencing standards like ETSI EN 303 645, EN 18031)
Public Charge Point Regulations 2023
The Public Charge Point Regulations 2023 came into effect with staggered implementation dates:
- Transparent pricing (displaying pence/kWh with no hidden fees or mid-session price increases): Effective immediately from 24 November 2023
- Main requirements including contactless payment (≥ 8 kW), 99% uptime for rapid chargers, and open data sharing: Effective from 24 November 2024
- Roaming/payment provider connections enabling cross-network payment: By 2025, public networks needed to connect to at least one roaming payments provider
Key requirements include:
- Contactless payment: Charge points ≥ 8 kW must accept card-based, app-free contactless payment methods
- Reliability / availability: Rapid chargers must achieve 99% uptime with reporting obligations
- Transparent pricing: Display pence/kWh with no hidden fees or price increases mid-session
- Open data / interoperability: Share location, status, connector type, pricing and network data in machine-readable format
- Roaming/payment provider: By 2025, public networks had to connect to at least one roaming payments provider so EV drivers can pay across networks
These regulations push the industry towards a baseline of interoperability, payment flexibility and transparency.

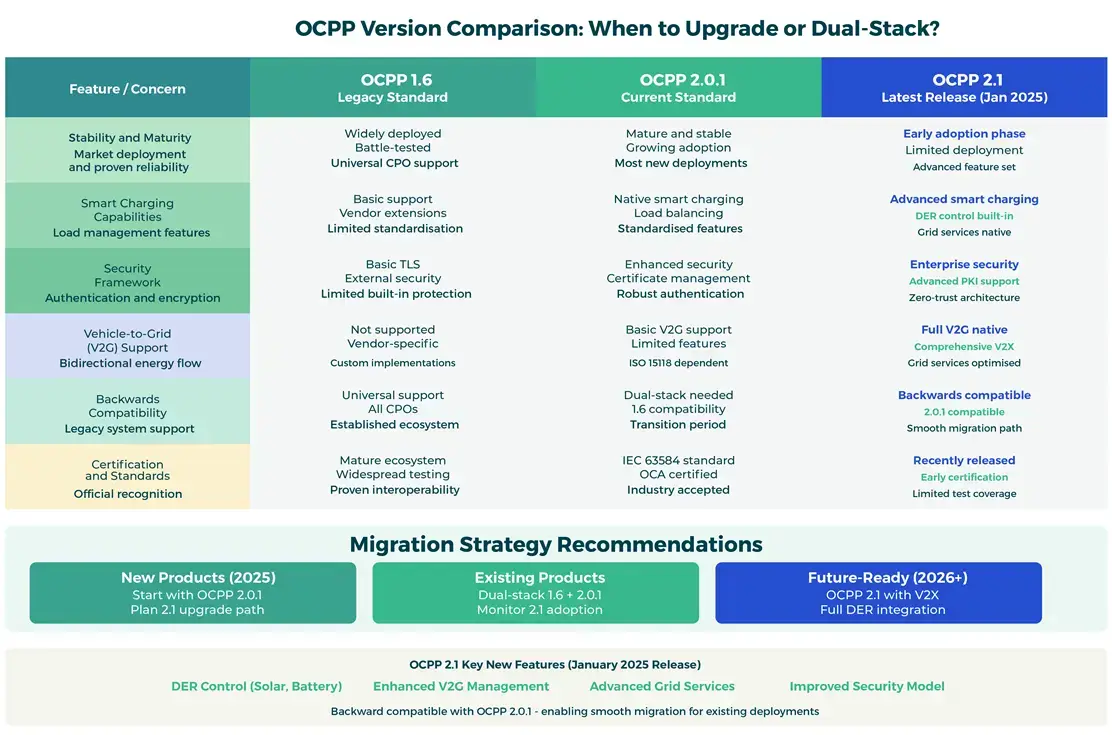
When Should Manufacturers Migrate to OCPP 2.1? Can I Run Dual-Stack (1.6 + 2.1) Simultaneously?
OCPP remains the language of choice between charger hardware and back-office systems, so choosing which version(s) to support is a strategic decision with long-term implications.
OCPP 2.1 was released in January 2025, building on 2.0.1 by adding DER (Distributed Energy Resources) control and enhanced V2G support, among other features.
It’s an extension of OCPP 2.0.1, meaning current applications will continue to work in OCPP 2.1 with minimal changes.
Best Practice Guidance
- For new products: Start with OCPP 2.1 support built in, with a backward compatibility shim to 1.6 for legacy network operators
- Use feature flags in your firmware so you can enable or disable advanced features without requiring new hardware revisions
- Early testing across major CPO platforms is essential; OCPP implementations vary significantly between providers
- Leverage Versinetic’s OCPP modules or field-tested reference integrations to reduce reinvention and accelerate certification
Hardware, Firmware and Test Implications
Standards are nothing without solid hardware and firmware that deliver correctly under real-world conditions.
Hardware Design Considerations
- Incorporate secure elements / hardware cryptography modules to offload heavy crypto tasks and protect certificate storage
- Include support for a PLC (PowerLine Communications) modem in your design—ISO 15118 requires this additional component to enable communication between the EV and EVSE
- Ensure your processor selection can support TLS 1.3 and certificate handling without performance degradation
- Design for OTA firmware updates with rollback safeguards to enable field updates
Pay attention to EMC, safety (CE / UKCA), insulation, current / temperature ratings, and connector durability - Plan for accessibility compliance (PAS 1899) for public charge point installations
Firmware Considerations
- Modular architecture: Keep communication stack (ISO, OCPP) decoupled from application logic for easier updates
- Fallback / failover: If ISO 15118 handshake fails, fallback to legacy IEC 61851 mode gracefully
- Logging, diagnostics, self-test routines, and comprehensive exception handling
- Security hardening: Side-channel protection, certificate revocation checking, firmware signature verification, best cybersecurity practices
- Interoperability test harnesses with multiple EV OEMs and CPO systems
Testing & Validation
- Conformance testing (protocol correctness against specifications)
- Compliance testing to standards
- Interoperability testing (EVs from different manufacturers, multiple CPO systems)
- Load testing (peak conditions, network delays, concurrent sessions)
- Field trials (real-world environment, edge cases, extended duration)
- Security penetration testing: Independent research shows weaknesses in some deployed systems, making ongoing security assessment critical
Versinetic has assisted OEMs with ISO 15118 integration, running comprehensive lab and field test suites, and developing diagnostic modules that achieve compliance across EU and UK borders.
This gives us first-hand insight into typical failure modes – certificate expiry handling, handshake timing issues, and fallback logic problems.
How to Future-Proof Your EV Charger Roadmap
Given the velocity of change, here are pragmatic steps your team should embed now:
- Adopt ISO 15118 support early (even if optional at launch); retrofitting later is significantly more costly and complex
- Design modular firmware and hardware abstraction layers so that new standards or protocol versions can slot in without wholesale redesigns
- Engage in standards bodies/alliances (BEAMA, CharIN, OCA); being upstream gives you foresight into coming changes before they become mandates
- Plan certification, interoperability, and pilot deployments early; don’t wait until you’re shipping production hardware to discover compatibility issues
- Choose partners/stacks with proven field use (such as Versinetic) to avoid reinventing complex protocol implementations
- Monitor and respond to security research. The charging ecosystem is a live target for malicious actors, and staying ahead of vulnerabilities protects your brand
By doing this, you reduce the risk of obsolescence, avoid expensive redesign cycles, and maintain attractiveness to CPOs and fleet operators who increasingly demand standards compliance as a baseline requirement.
Proven Solutions for Complex EV Charging Standards Implementation
Here’s how Versinetic can serve your roadmap:
We provide field-proven software modules that you can embed directly into your firmware, dramatically reducing development time and certification risk.
Evaluation kits and ISO 15118-compatible PLC modem boards enable rapid prototyping and proof-of-concept development.
We have run test labs with EV OEMs, CPO platforms and back-end systems, giving you access to the real-world validation that specifications alone can’t provide.
Aligning your product roadmap with UK regulations, BEAMA, CharIN requirements, and OCPP/OCA engagements ensure you’re building to the right targets.
We help upgrade existing charger fleets with ISO 15118 integration and security patches, protecting your installed base investment.
We have supported multiple projects across the UK and Europe – our engineers have been active contributors in OCPP working groups, BEAMA committees and CharIN task groups, giving us direct insight into standards evolution before it impacts the market.
FAQ — Common Manufacturer Queries
How long does ISO 15118 integration take?
It depends on your partner, the scope (AC / DC, which use cases), and test cycle throughput. In practice, 3–9 months is a realistic range including interoperability trials. Starting with proven reference implementations can cut this timeline significantly.
Can I retrofit older chargers to support Plug & Charge?
Not usually. ISO 15118 requires the charger to have a PLC modem. If the charger was designed with one or with the ability to add one, then it may be possible to add support for ISO 15118 / Plug & Charge through firmware updates. Otherwise, hardware redesign is necessary.
Does ISO 15118 require specific hardware?
You will need a PLC modem (such as the Qualcomm QCA7005 or Lumissil CG5317) and a processor with enough spare performance to run the ISO 15118 state machine and support for TLS 1.3. No single chipset is currently mandated, but cryptographic capabilities are essential.
What certificate authorities / PKI frameworks are available?
Each global region can have a number of PKIs, each with a Certificate Authority. In Europe, Hubject operates one of the major PKIs for Plug & Charge. Versinetic can help integrate with or operate in whichever region/ecosystem you plan to deploy in, reducing your integration burden.
Will OCPP 1.6 be deprecated?
While 1.6 is unlikely to vanish overnight, the trend is clear: most new features and support will centre around 2.1. Dual-stack or migration paths will likely become standard practice for manufacturers serving both legacy and next-generation networks.
Is Your Charging System Ready for These Changes?
Use this interactive EV standards checklist>>
UK EV Charging Standards 2026 Interactive Audit Tool
| Critical Area | Status | Immediate Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 15118 (Plug & Charge) Support |
Yes
In Progress
No | Integrate certified ISO 15118 stack |
| OCPP 2.0.1 Dual-Stack Ready |
Yes
In Progress
No | Update firmware/backend systems |
| Smart Charge Regulations Compliant |
Yes
In Progress
No | Add off-peak & security controls |
| Public Charge Point Regs Ready |
Yes
In Progress
No | Review payment & data requirements |
| Cybersecurity Audit Complete |
Yes
In Progress
No | Schedule penetration testing |
Pre-certified, field-tested implementation
Dual-stack support & backend integration
LinkRay & SiteManager load management
Expert consultancy & certification support
Pre-certified, field-tested implementations
Secure, standards-compliant designs
Expert guidance & certification support
Comprehensive validation services
🌐 Web: versinetic.com/contact
✉️ Email: getcharged@versinetic.com
📱 Phone: +44 121 828 9292
Book your free 30-minute Standards Readiness Consultation
Driving interoperability and innovation in EV charging infrastructure
versinetic.com | ISO 15118 • OCPP • Smart Charging & Load Management

Versinetic’s editorial team includes engineering specialists who were among the developers that supplied EV chargers for the 2012 London Olympics.
Further Reading & Sources
- Smart Charge Points Regulations 2021 – GOV.UK
- Electric Vehicles (Smart Charge Points) Regulations 2021 – Legislation.gov.uk
- The Public Charge Point Regulations 2023 – GOV.UK
- Electric Vehicles (Smart Charge Points) Regulations 2021 Implementation Guidance – GOV.UK
- Approved Document S: Infrastructure for the charging of electric vehicles – GOV.UK
- ISO 15118 Road vehicles — Vehicle to grid communication interface
- CharIN – ISO 15118 Plug & Charge
- OCPP 2.0.1 Specification – Open Charge Alliance
- OCPP 2.1 Release – Open Charge Alliance
- IEC 61851-1:2017 Electric vehicle conductive charging system
- IEC 62196 Plugs, socket-outlets, vehicle connectors and vehicle inlets
- PAS 1899:2022 Electric vehicles – Accessible charging – Specification
- Energy Saving Trust: Accessible EV Charging
- ETSI EN 303 645 – Cyber Security for Consumer Internet of Things
- IEA Global EV Outlook 2025
- Zap-Map UK EV Charging Statistics
- UK Parliament Public Accounts Committee Reports
- Versinetic Company Profile
- Charging on the Go: Public EV Infrastructure and Payments Whitepaper 2024
- Ultra-Fast Charging vs Grid Realities: A Practical Roadmap for UK Infrastructure Developers



