TL;DR: Your Guide to Local-Load Ready EV Charging
- Hardware Readiness: For new UK kerbside EV charging projects, grid capacity is a key limiting factor and dynamic load balancing solutions are needed to overcome power management challenges
- Dominance of Slow Charging: 56% of all UK public chargers are slow-speed (3-8 kW) units deployed on-street. For these installations, intelligent power-sharing between multiple units is an immediate operational necessity.
- The Market Opportunity: A major opportunity gap exists in regions outside of London and the South East. Kerbside charging is the only viable option for 9.3 million UK households that do not have a driveway.
- Accelerated Deployment: Charge Point Operators (CPOs) and manufacturers can use white-label hardware solutions to meet tightening project timelines, reducing time-to-market by up to 40%
Table of Contents
As the UK government announces a fresh £63 million boost for kerbside and depot EV charging infrastructure, there’s renewed momentum behind on-street charging projects.
But funding alone won’t overcome a critical barrier: limited local grid capacity.
At Versinetic, we support charge point manufacturers, CPOs and installation firms building scalable EV charging networks.
And as this new wave of on-street charging deployments begins, the core question facing you is this:
Is your hardware designed to handle the local load challenge—efficiently, compliantly, and without crippling civil engineering costs?
Urban Networks Are Not Ready for High-Density Charging
The government’s latest round of investment includes:
- £25 million for kerbside charging projects via the Local EV Infrastructure (LEVI) Fund
- £30 million to electrify fleet depots
- £8 million to support NHS fleet charging deployments (Source: GOV.UK, July 2025)
This cash injection arrives as the UK charging infrastructure enters a rapid expansion phase.
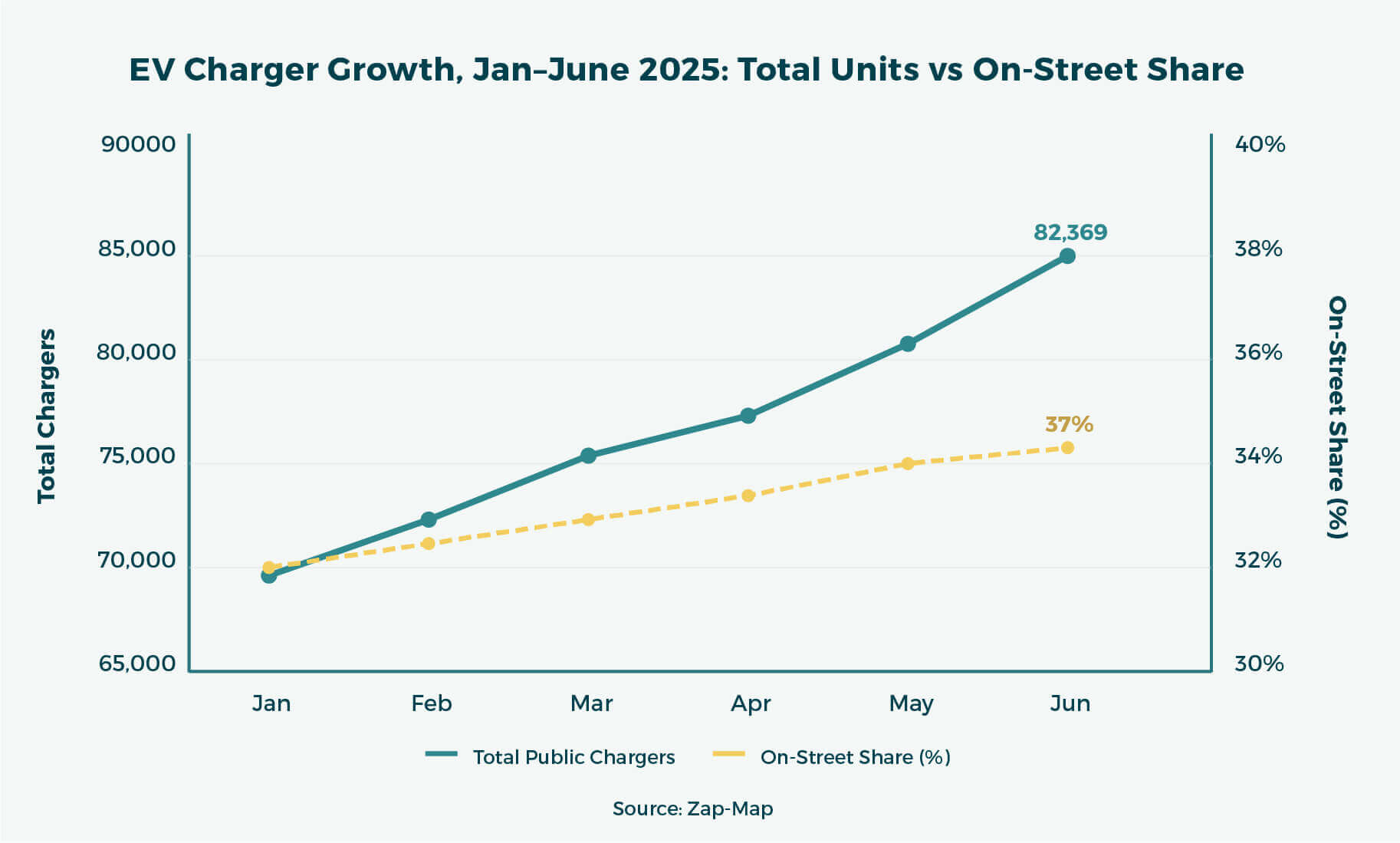
As of 1 April 2025, the UK had:
- 76,507 public EV chargers,
- Of which 28,316 (37%) were on-street units, up from 36% in January (Source: DfT, April 2025)
By 30 June, total chargers reached 82,369 across 40,479 locations, with 1,371 added in June alone, according to Zap-Map.
However, growth brings strain.
Many urban substations were never designed to support the heavy load of high numbers of 3 phase 22KW chargers, without intelligent load management numbers would limited be to prevent overloading the supply.
Why Local Load Management Must Be Built In
At Versinetic, we’ve helped OEMs and CPOs deploy load-aware infrastructure through our SiteManager and LinkRay systems, enabling dynamic power sharing between multiple chargers installed on a single low-voltage connection.

Technical Example
A typical residential feeder allows 32 kW headroom.
Using LinkRay, four 7 kW chargers can be installed, with load dynamically balanced per active session.
This avoids overloads and defers costly network upgrades.
According to government data (Source: DfT Charging Statistics, April 2025), the current split of public EV charger speeds is as follows:
- 56%: Slow (3–8 kW)
- 24%: Fast (8–49 kW)
- 20%: Rapid/Ultra-rapid (50 kW+)
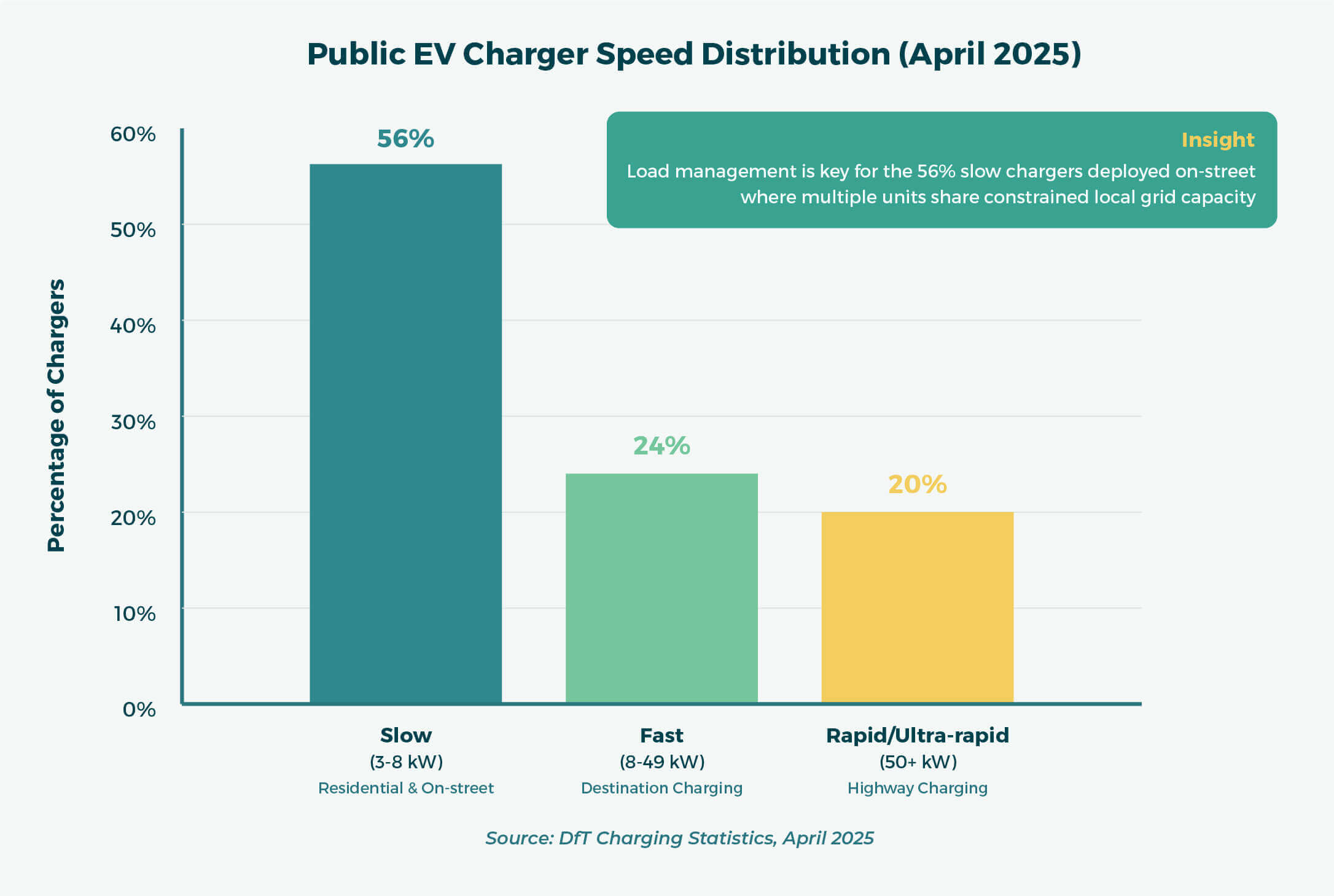
This skew towards low-power devices reflects the dominance of residential and on-street use cases.
Load management is not a future consideration—it’s an operational necessity.
Design and build kerbside chargers fast with White-Label Hardware Made for the Street
Procurement timelines for LEVI-funded projects are tightening. CPOs and charge point manufacturers are under pressure to deliver scalable, compliant, and serviceable chargers—fast.
Versinetic offers:
- White-labelled hardware and software solutions, pre-engineered for kerbside environments
- Modular electronics and software stacks
- Fast integration with your cloud platform via OCPP 1.6J & 2.0.1.
Our controller boards, embedded firmware and diagnostics modules are already helping EV charge point manufacturers reduce time-to-market by up to 40%, with robust supply chain support and tailored enclosures.
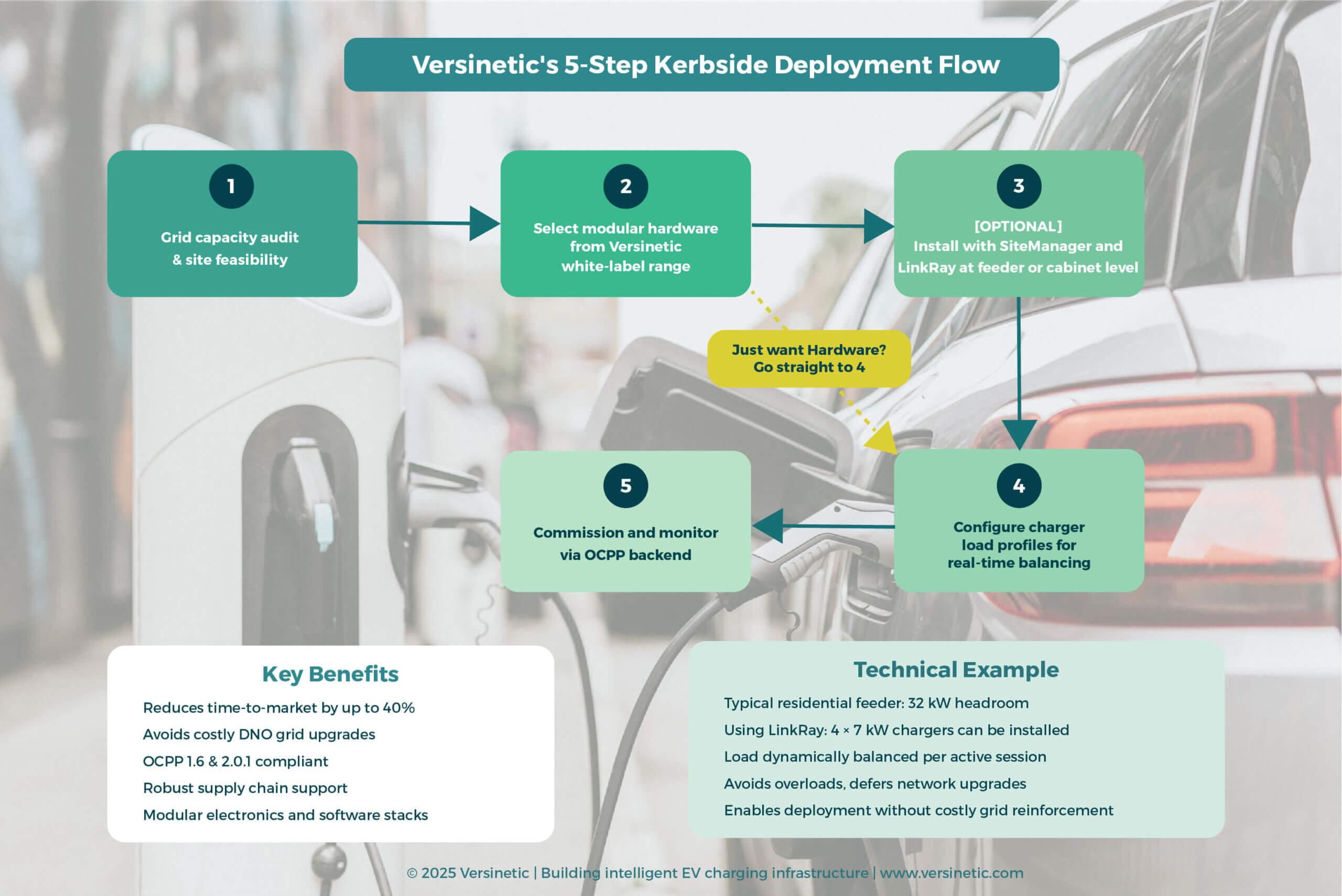
⚡ Versinetic’s 5-Step Kerbside EV Charging Deployment Flow
For operators looking to move quickly under the new funding frameworks, we recommend the following process:
- Step 1: Grid capacity audit & site feasibility
- Step 2: Select modular hardware from Versinetic's white-label range
- Step 3: Install with SiteManager or LinkRay at feeder or cabinet level (Optional extra)
- Step 4: Configure charger load profiles for real-time balancing
- Step 5: Commission and monitor via OCPP backend
Target the Right Locations - Not Just the Obvious Ones
According to a 2024 Parliamentary report, 43% of the UK’s charging devices are located in London and the South East, leaving rural and northern areas underserved.
Meanwhile, 9.3 million UK households have no driveway or garage, meaning kerbside EV charging is their only viable option.
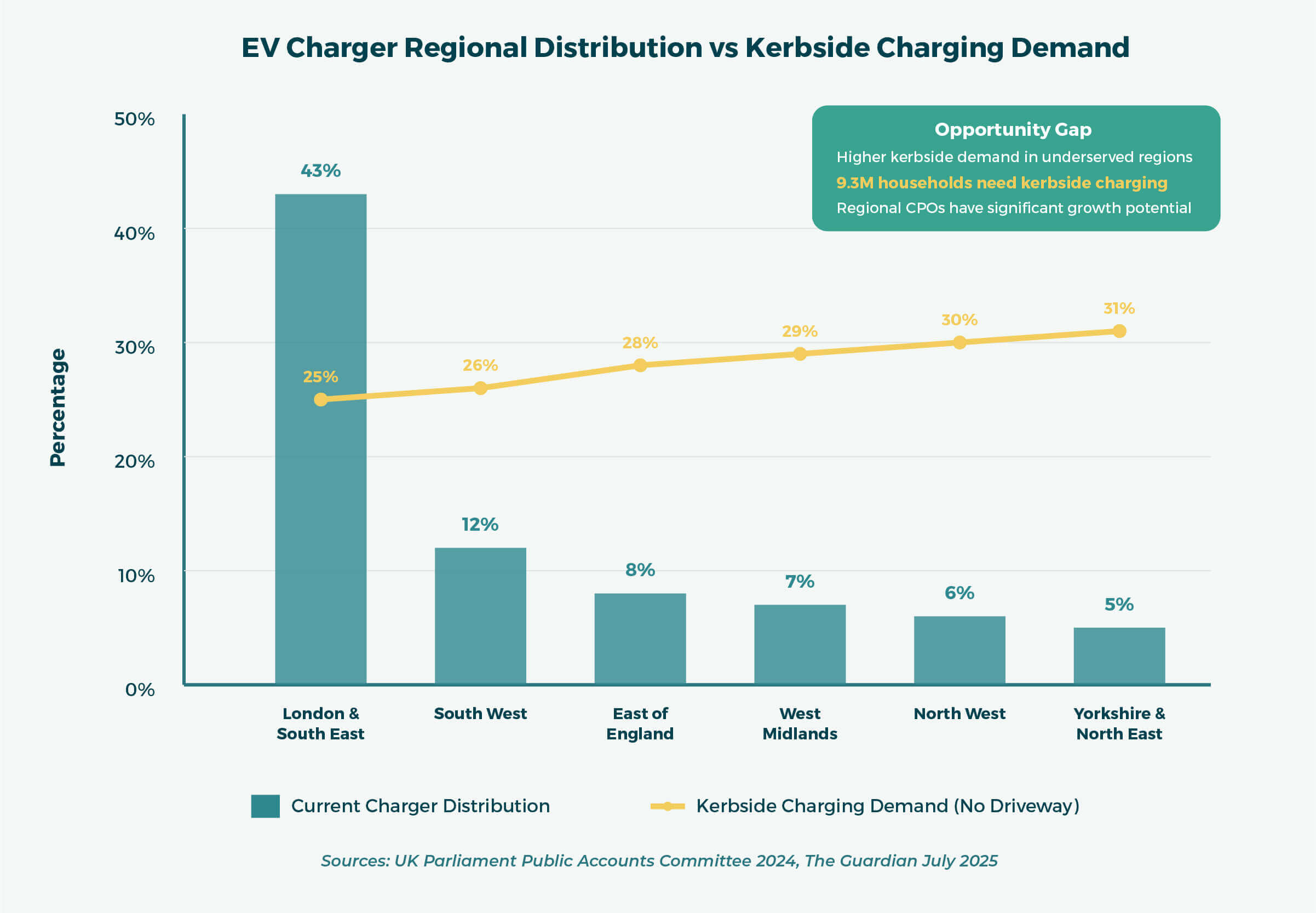
This gap represents opportunity—particularly for regional CPOs and OEMs offering flexible hardware and intelligent grid-ready systems.
Are Your Products Kerbside Ready?
with embedded load management tools for your next rollout.
Let’s build kerbside charging infrastructure that works - intelligently and at scale.
Kerbside EV Charging FAQs
What’s the minimum grid capacity needed for kerbside EV charger installations? A: Typical residential feeders provide 32 kW headroom. Using Versinetic’s LinkRay load management, you can install four 7 kW chargers on a single connection with dynamic load balancing, avoiding costly DNO upgrades that can cost hundreds of thousands of pounds per site. LinkRay is primarily targeted at large-scale, commercial sites.
A: Local load management works independently at the feeder or cabinet level, providing instant response times and failsafe operation even during connectivity issues.
Cloud systems introduce latency and dependency risks that can compromise grid safety during peak demand periods.
A: Yes, Versinetic’s SiteManager and LinkRay systems are designed for both new installations and retrofitting existing networks.
Our modular approach allows integration with OCPP 1.6 and 2.0.1 compliant chargers without replacing the entire infrastructure.
A: Our clients generally see ROI within 12-18 months through avoided DNO upgrade costs and the ability to deploy 40% more chargers per site.
Load management also enables dynamic pricing strategies that can increase utilisation by up to 117%.
A: Smart load management optimises power distribution based on actual demand. Users experience minimal impact; charging sessions are dynamically adjusted to maximise throughput while staying within grid limits. Most importantly, it prevents service interruptions from grid overloads.
A: Key requirements include PAS 1899 accessibility standards, street furniture compliance (IP ratings, vandal resistance), and evolving LEVI/OZEV guidance.
Our white-label hardware is pre-engineered to meet these standards, reducing compliance risk and approval timelines.
A: With modular electronics, embedded firmware, and OCPP compliance built-in, Versinetic’s white-label hardware and software stacks reduce time-to-market by up to 40%.
A: Kerbside chargers require minimum IP54 rating for weather protection, with IP65+ preferred for coastal areas.
Essential features include reinforced cable management, tamper-proof housings, impact-resistant screens, and secure payment card readers. In the most part this is reliant on the charger manufacturer.
A: Multi-connectivity approaches are crucial. Our hardware supports 4G, Wi-Fi, and Ethernet with automatic failover. We also implement offline payment capabilities and local data storage to maintain basic operations during connectivity outages.
A: AC charging (3-22 kW) dominates kerbside deployments (56% of public chargers are slow AC units) due to lower infrastructure costs and longer dwell times for residential parking. DC fast charging creates grid strain and higher costs. Versinetic’s modular approach allows mixing both technologies based on specific location requirements and available grid capacity.
A: Modular design is key. Versinetic’s charging systems use replaceable communication modules, upgradeable firmware, and standardised payment interfacing. This allows cost-effective adaptation to new standards (like ISO 15118 Plug & Charge) without replacing entire units. Our clients save ~30% on upgrade costs compared to monolithic charger designs.

Dunstan is the founder of EV charger design consultancy, Versinetic. He is a chartered electronics engineer who has been providing design, production support and consultancy to businesses around the world for over 30 years. Dunstan graduated from Cambridge University with a degree in electronics engineering in 1992. After working in the industry for several years, he co-founded multi-award-winning electronics engineering consultancy ByteSnap Design in 2008. He then went on to launch international EV charging design consultancy Versinetic during the 2020 global lockdown. An experienced conference speaker domestically and internationally, Dunstan covers several areas of EV charger design and electronics product development, including load balancing, V2G, IoT, integrated software design and complex project management.
In his spare time, Dunstan enjoys hiking and astronomy.




