⚡ TL;DR – EV Charging Infrastructure 2026 Trends: Quick Answers
What are the biggest EV charging infrastructure trends for 2026?
V2G becomes mandatory for UK commercial installations above 22kW from March 2025, cybersecurity emerges as a primary selection criterion, and ultra-fast charging proves economically unviable for widespread deployment despite headlines.
Is ultra-fast charging the future of EV infrastructure?
Ultra-fast charging (5-minute charging requiring 756kW) faces major infrastructure barriers, as each charger needs power equivalent to 350 homes. The real EV advantage is home/work charging convenience, not replicating petrol station paradigms.
What cybersecurity risks affect EV charging infrastructure in 2026?
Oslo tests revealed Chinese-made EVs can be remotely disabled. Hardware manufacturers must now verify supply chains, document communication protocols, and implement local control fallbacks as primary selection criteria.
Versinetic’s engineering team has been reflecting on where the EV charging industry is heading in 2026.
Three themes keep surfacing in our conversations: tightening regulations that actually have teeth, cybersecurity threats that can no longer be ignored, and a growing disconnect between headline-grabbing charging speeds and what the infrastructure can realistically deliver.
If you’re responsible for EV charging projects, whether you’re evaluating hardware, planning regional rollouts, or ensuring compliance, understanding the trends shaping 2026 will help you avoid expensive missteps.
Here’s what our engineering consultants are watching closely.
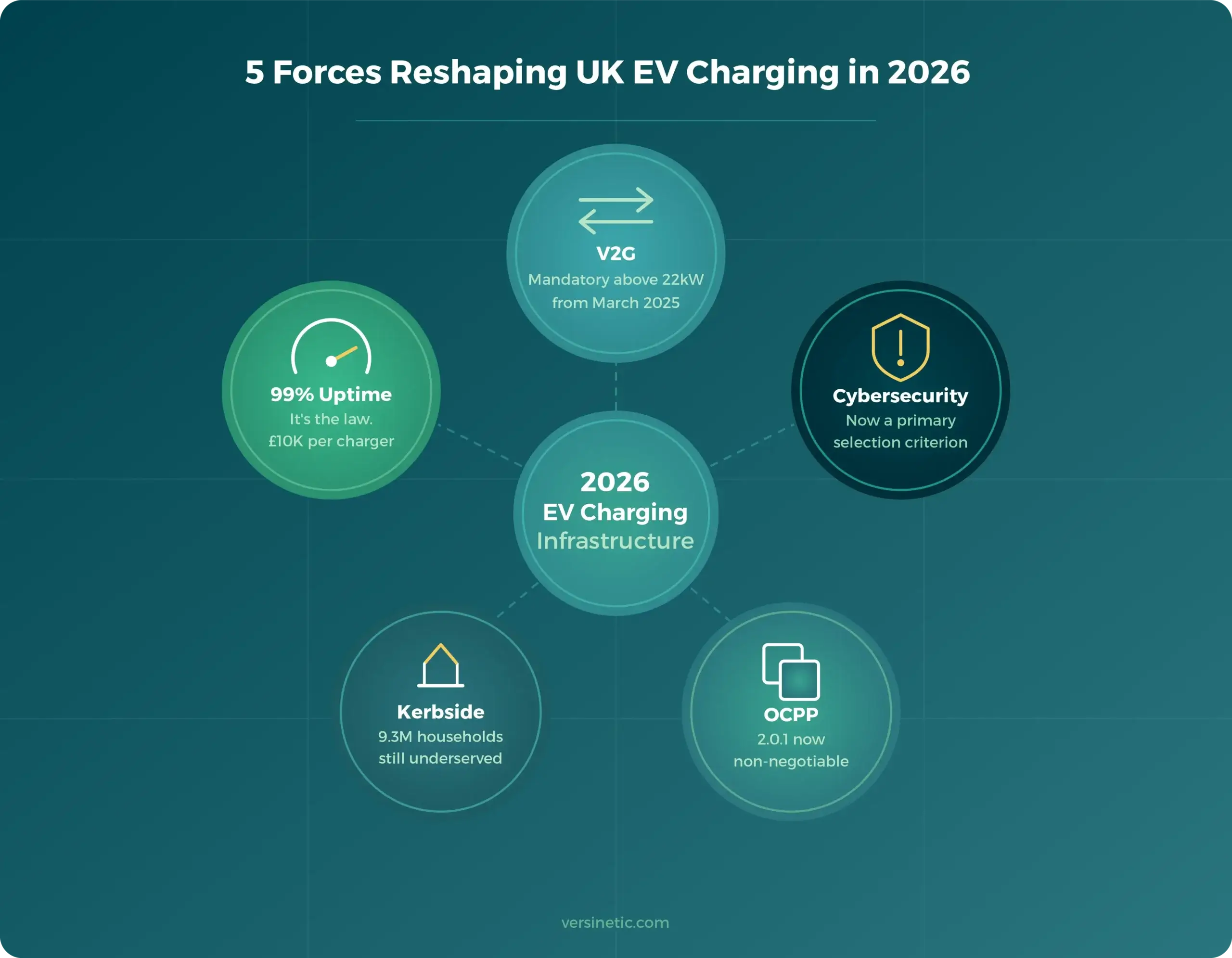
2026 Trend #1 - The UK's 99% Uptime Rule Will Force Industry Consolidation
Here’s the uncomfortable reality: The UK’s 99% uptime requirement for rapid chargers (50kW+) isn’t a target; it’s the law.
And it’s going to reshape the entire CPO market in 2026.
At 99% uptime, your charger can be broken for only 87.6 hours per year.
That’s roughly 7 hours per month.
For a CPO running 100 rapid chargers across dispersed locations, that’s a massive operational challenge.
Miss the target? You’ll face a £10,000 fine per non-compliant charger from the Office for Product Safety and Standards. For smaller operators, these penalties aren’t just expensive -they could put you out of business.
Who's most at risk?
Regional operators with 10-30 chargers face the harshest economics. You’re too small for dedicated 24/7 maintenance teams, but too large to manage everything reactively when things go wrong.
We’re predicting 2026 will see the first wave of smaller CPOs either acquired by larger networks with established maintenance capabilities, or exiting the market entirely.
Action Tip:
Regional CPOs have two choices:
- Invest in remote monitoring and predictive maintenance systems that can catch problems before they become fines
- Seriously consider partnership opportunities with larger networks before market conditions force distressed sales
Hardware suppliers: your customers will increasingly demand chargers with comprehensive diagnostics and self-reporting capabilities. Build that in from day one, not as an afterthought.
Source: UK Public Charge Point Regulations 2023, Office for Product Safety and Standards
2026 Trend #2 - Kerbside Charging Remains the Sector's Biggest Challenge
Despite all the urgency, kerbside charging infrastructure for the 9.3 million UK households without off-street parking will continue to lag dramatically behind need throughout 2026.
Why the economics don’t work yet
Kerbside chargers face a brutal business model:
- Lower revenue than forecourt rapid chargers (overnight charging at lower rates)
- Expensive installation (trenching, ducting, DNO upgrades can cost tens of thousands per unit)
- Complex approval processes that can take months with local authorities
Yet this is exactly where equitable EV access depends.
The geographic gap is widening
Currently, 43% of UK charging devices sit in London and the South East. Rural and northern areas remain significantly underserved. Without major policy intervention, that gap will likely widen before it narrows.
What to watch in 2026
Local authorities deploying LEVI (Local Electric Vehicle Infrastructure) funding proactively, and those piloting innovative models like lamppost charging conversions or pop-up kerbside units. These early movers will establish the templates others eventually follow.
The opportunity:
This represents both the biggest infrastructure challenge and the largest addressable market opportunity for innovative CPOs and hardware manufacturers. Solutions that dramatically reduce installation costs or work within existing street furniture will find eager customers.
Sources: The Guardian, July 2025; UK Parliament Public Accounts Committee Report 2024

2026 Trend #3 - V2G Moves from Pilot Projects to Legal Requirement
2026 is the turning point
From March 2025, Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) functionality became mandatory for new commercial charge point installations rated above 22kW in the UK.
We anticipate 2026 will be remembered as the year V2G moved from experimental technology to commercial standard. Here’s what to expect:
- Q1-Q2 2026: Manufacturers rush to ensure commercial charger products meet V2G requirements. Expect some product launch delays as companies retrofit bidirectional capability.
- Q3-Q4 2026: First commercial building installations begin demonstrating V2G revenue through demand response programmes.
- Throughout 2026: Tesla (all vehicles), General Motors (full EV lineup), and BMW (iX3 and Neue Klasse) deliveries scale the V2G-capable vehicle population significantly.
Why this matters more than charging speed
V2G addresses fundamental grid stability challenges as renewable generation creates supply variability. With potentially 250 million EVs globally by 2030, vehicle batteries represent distributed energy storage capacity without needing additional infrastructure investment.
The global V2G market, valued at approximately £11.4 billion in 2024, is projected to reach £129.8 billion by 2034, representing 27% annual growth.
UK leads the way
The UK pioneered V2G development through projects like VIGIL (Vehicle-to-Grid Intelligent Control), funded by Innovate UK and BEIS.

Versinetic, as a spin-out from ByteSnap Design, inherited this V2G expertise from the award-winning VIGIL project, bringing proven technology to commercial deployment.
Action Tip:
If you’re specifying commercial charging hardware in 2026, V2G readiness isn’t optional above 22kW – it’s legally required. Beyond compliance, early adopters who establish V2G revenue streams through demand response will gain competitive advantage as the business model matures.
Sources: UK Smart Charge Points Regulations 2021 (updated 2024); Wood Mackenzie Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Forecast 2025; VIGIL project
2026 Trend #4 - Cybersecurity Becomes a Deal-Breaker in Hardware Selection
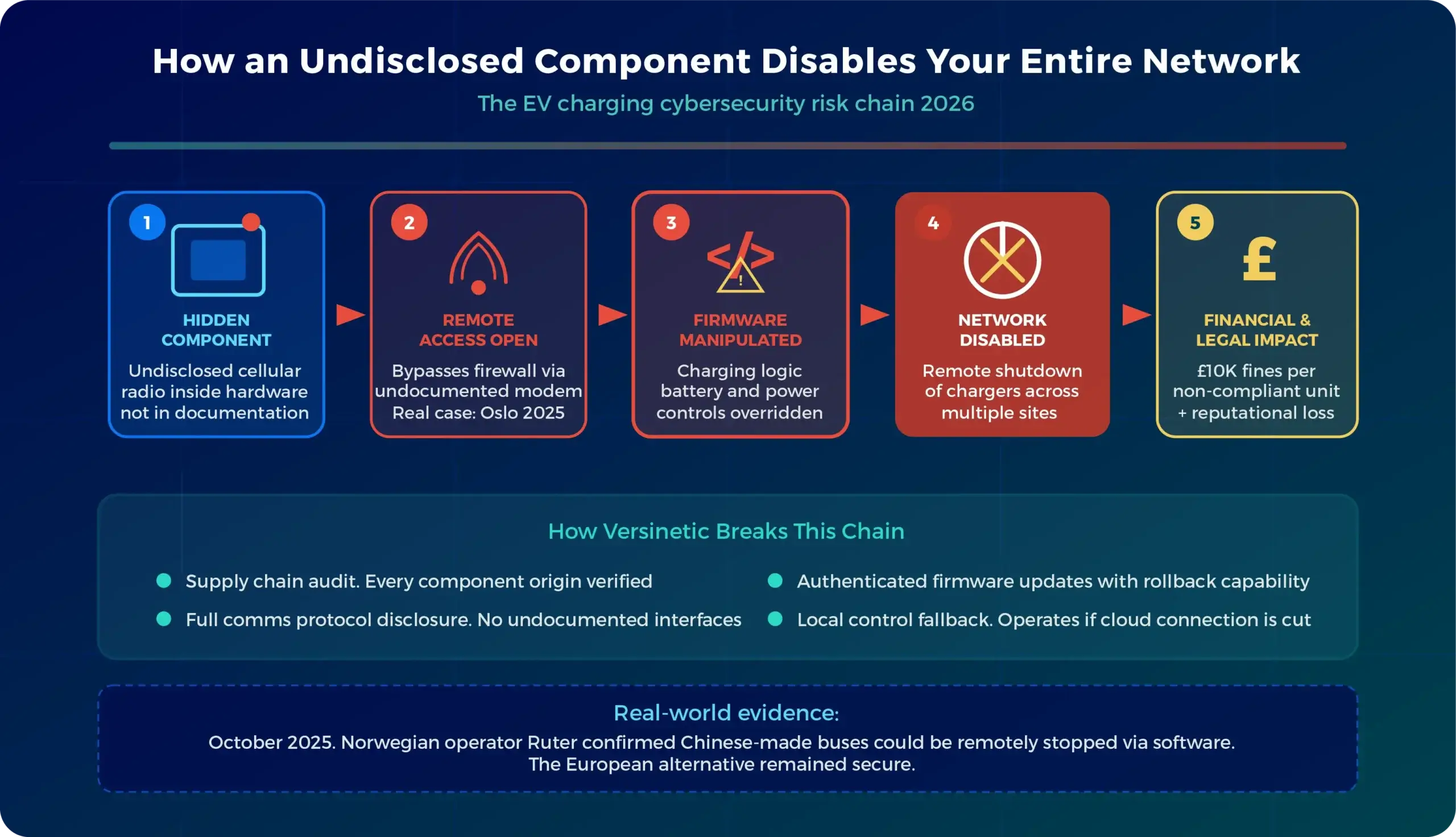
In October 2025, Norwegian transport operator Ruter revealed something alarming:
Chinese-made electric buses could be remotely stopped and disabled by their manufacturer.
The European bus they tested remained secure; the Chinese bus could be manipulated remotely through software updates, diagnostics, and battery control systems.
This wasn’t an isolated incident. In May 2025, US energy officials discovered undocumented communication devices, including cellular radios, hidden inside Chinese-made solar power inverters.
These components, not disclosed in product documentation, could potentially bypass firewalls designed to block unauthorised access.
What we expect in 2026
- Q1-Q2: UK government publishes formal guidance on acceptable supply chain origins for critical EV infrastructure
- Q2-Q3: Major CPOs implement mandatory cybersecurity audits in procurement processes
- Throughout 2026: Hardware manufacturers face pressure to demonstrate third-party security testing and supply chain transparency
Those unable to provide comprehensive documentation will lose market access.
Scale of the Risk: Europe has over 200 gigawatts of solar power capacity connected to Chinese-made inverters. Security experts warn that remotely controlling just 3-4 gigawatts could disrupt entire regions.
The same vulnerabilities exist in EV charging infrastructure.
Action Tip:
Review your current hardware suppliers’ ability to document:
- Communication protocols – every connectivity feature fully disclosed
- Firmware update security – authenticated, verified updates with rollback capability
- Local control fallbacks – ability to operate disconnected from external networks
- Supply chain audits – component origin verification, particularly for communications modules
Yes, this will increase procurement costs initially. But the alternative, equipment that could be remotely disabled, is both commercially and legally untenable.
Sources: Aftenposten (Norwegian newspaper), October 2025; Reuters investigation into Chinese inverters, May 2025; UK Department for Transport statements
2026 Trend #5 - OCPP Compliance: No Longer Optional
The standards baseline is rising fast. Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) compliance is completing its journey from competitive advantage to absolute requirement throughout 2026.
With hundreds of new EV models expected by 2027, compatibility can’t be guaranteed through ad-hoc testing. The industry now runs regular interoperability testing events where manufacturers verify that any vehicle can charge at any compliant charger without communication failures.
What changes in 2026
- OCPP 1.6 becomes the absolute minimum: Products without it are effectively unmarketable to professional CPOs
- OCPP 2.0.1 adoption accelerates: Enhanced security features (ISO 15118-20 integration) and smart charging capabilities drive upgrade pressure
- ISO 15118-20 security becomes expected: PKI authentication, encrypted communications, and plug-and-charge functionality move from premium features to baseline requirements
Commitment matters just as much as compliance
Go beyond just achieve compliance; instead, demonstrate a clear roadmap for standard updates.
OCPP is evolving; your hardware must keep pace or risk obsolescence within 2-3 years.
Action Tip:
Review your current charger specifications. If OCPP 2.0.1 isn’t on the roadmap, your equipment will be outdated by year-end. For installers, understanding OCPP version requirements in RFPs becomes essential; nowadays, clients tend specify minimum versions.
Sources: Open Charge Alliance Technical Documentation 2025; ISO 15118-20 Standard Published 2024
Versinetic's View: Building for the real 2026
At Versinetic, these predictions inform our product development and customer support strategies.
We’re not chasing ultra-fast charging specifications that require impractical infrastructure investment. We’re focused on what the market actually needs:
LocalLoad-Ready Hardware
Our intelligent load management helps you avoid costly DNO upgrade delays and installation bottlenecks.
OCPP 1.6/2.0.1 Compliance
Clear roadmap to emerging standards, including commercial V2G support built on our award-winning VIGIL project heritage.
Documented Security Protocols
Transparent supply chain information with every component origin verified, because cybersecurity is no longer optional.
Modular Design
Future capability additions without replacing infrastructure, protecting your investment as standards evolve.
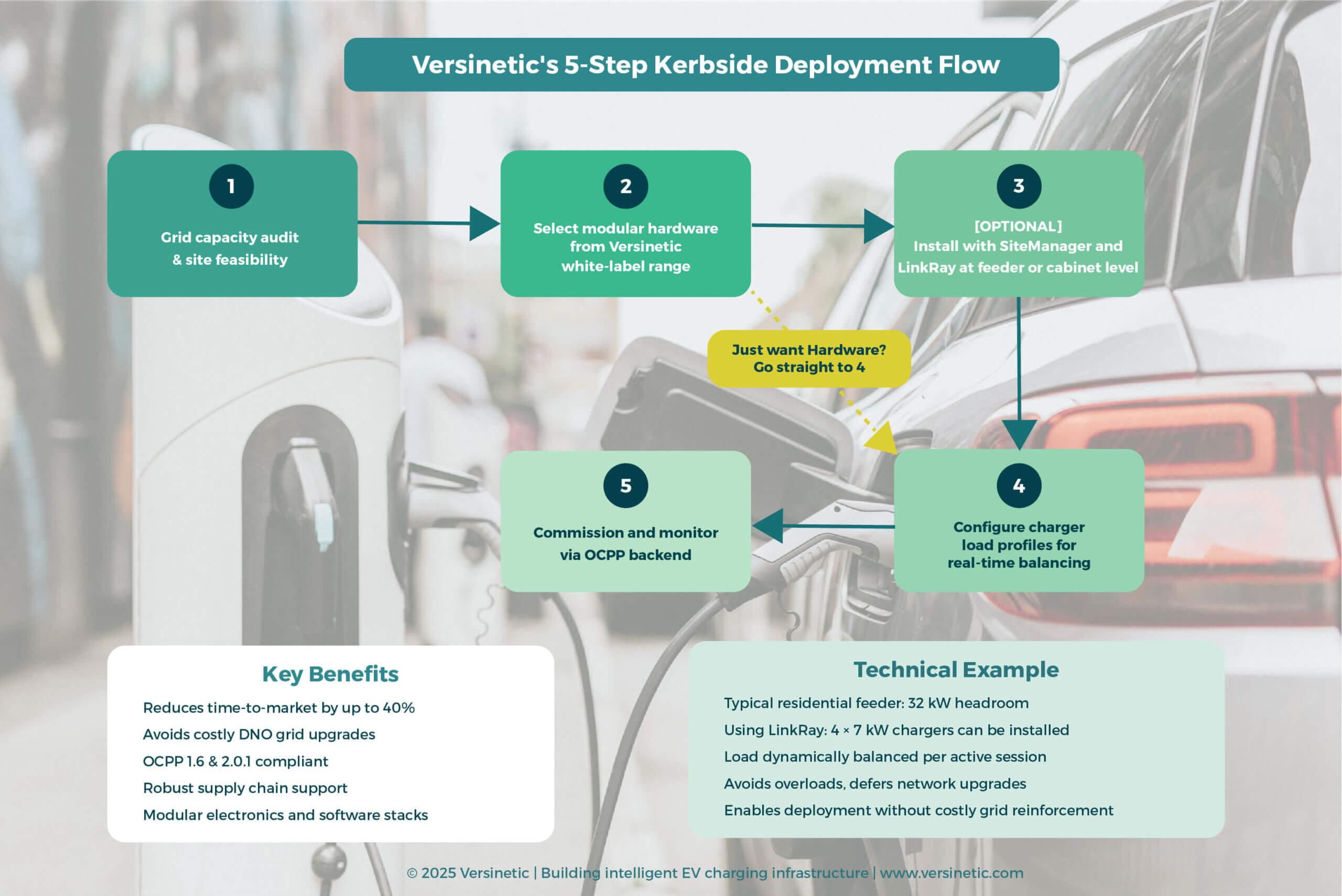
For kerbside deployments specifically – the real infrastructure challenge for those 9.3 million households without off-street parking – our five-step deployment process from grid capacity audit through commissioning accelerates time-to-market whilst maintaining compliance with UK Public Charge Point Regulations.
We’re solving the problems that actually exist: equitable access, grid-friendly load management, cybersecurity, and compliance.
These are the challenges that will define success in 2026.
Are your EV charger projects affected by these predictions?
Further reading
UK Regulations and Policy
- UK Public Charge Point Regulations 2023 – Official Guidance
- UK Smart Charge Points Regulations (updated 2024)
- Office for Product Safety and Standards (OPSS) Enforcement Policy
Market Forecasts and Industry Analysis
- Bloomberg New Energy Finance EV Charging Outlook 2025
- Wood Mackenzie Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Forecast
- International Energy Agency (IEA) Global EV Outlook 2025
Infrastructure and Deployment
- UK Parliament Public Accounts Committee Report 2024 on EV Infrastructure
- The Guardian: UK Kerbside Charging Analysis, July 2025
- Paren Q2 2025 US EV Fast Charging Report
Cybersecurity and Risk
- BeyondTrust 2026 Cybersecurity Predictions
- Aftenposten: Chinese Electric Bus Remote Shutdown Tests, October 2025
- Reuters investigation into Chinese inverters, May 2025
Technical Standards

Versinetic’s editorial team includes engineering specialists who were among the developers that supplied EV chargers for the 2012 London Olympics.



